BEB Treatment
The most effective treatment for BEB, Cranial dystonia and HFS to date, is minute doses of botulinum toxin (such as Botox® or Xeomin®) injected directly into the affected muscles. These injections weaken the muscles by blocking nerve impulses and give some improvement within days.
Treatment is usually repeated every 3 to 4 months, or as needed. Botulinum toxin injections are administered by specially trained neurologist, ophthalmologist or neuro-ophthalmogist.
In cases where botulinum toxin is not sufficiently effective, other treatments may prove helpful. Certain drugs may weaken or diminish spasms and there are several surgical options.
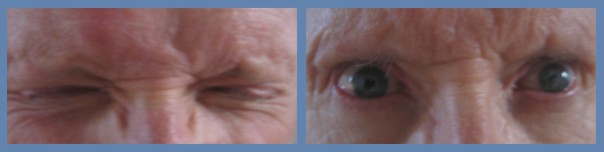
This pair of images shows a male patient, before and after a treatment with
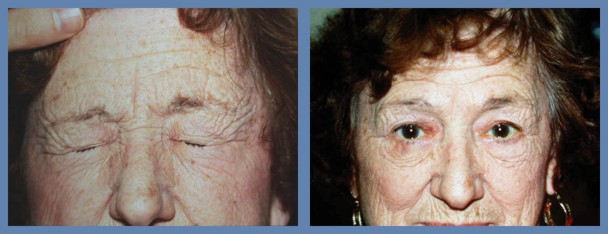
These images show a female patient, before and after treatment.
One surgical option for BEB is a myectomy, whereby a portion of the muscles controlling the eyelids is removed. People affected with apraxia of eyelid opening may have a device known as a frontalis sling inserted, which connects the eyelids to the frontalis muscle of the forehead in order to raise the eyelids. People with HFS may be helped with micro-vascular decompression surgery to take pressure off the affected nerve.
Prognosis
Generally, treatment is refined over time, as the individual and their medical professionals gradually find the specific approach that best helps their situation.
